Quicker Recovery. Surgical Excellence. Minimally Invasive, Maximum Care
Precision Surgery for a Healthier Tomorrow: Leading in Minimally Invasive Surgical Care
Dr. Praveen Verma, a highly skilled General and Laparoscopic Surgeon at Verma Hospital, is dedicated to providing exceptional surgical care with a focus on minimally invasive techniques. With extensive experience and a commitment to patient well-being, Dr. Verma ensures the highest standards of medical excellence and personalized treatment for every patient.
What Is General surgery ?
General surgery handles disorders of the abdominal region, chest area, skull and neck region, skin, and ligaments using an extensive array of surgical procedures. A wide range of diseases, such as disease of the gallbladder, appendix infection, hernias, and most types of cancer are identified and addressed by general surgeons. They also perform a wide range of surgeries that are minimally invasive, like as laparoscopy and endoscopy.
General surgeons are highly experienced and informed in all areas of surgical treatment, from pre-operative testing and planning to actual surgical operation and post-operative care. They partner with healthcare professionals, other physicians, and other healthcare professionals to provide their patients comprehensive care.
The field of general surgery continues to evolve with advancements in technology, minimally invasive techniques, and interdisciplinary approaches to patient care.
The Verma Hospital’s Laparoscopic and General Surgery Department will be delighted to have you visit! Our hospital uses both complete-scope preferred surgical treatment services and contemporary laparoscopic techniques to provide high-quality surgical treatments. Dr. Praveen Kumar Verma, our medical expert, along with our personalized and patient-centered approach to healthcare, are some of our best features
Disease Under General Surgery :-
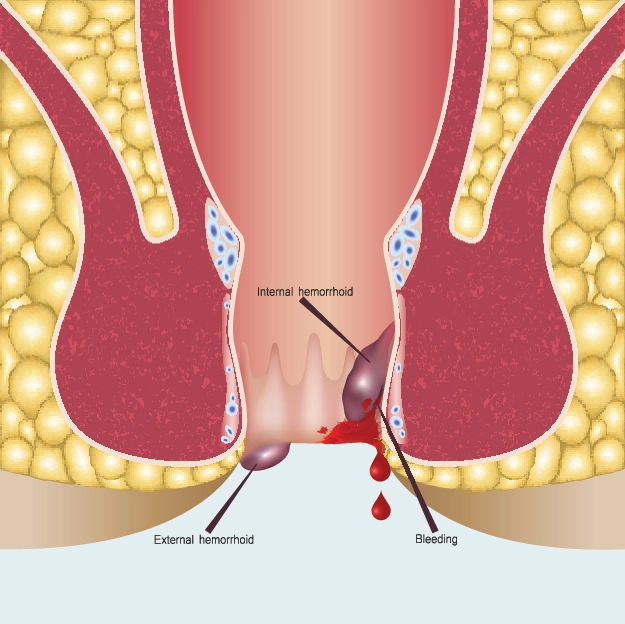
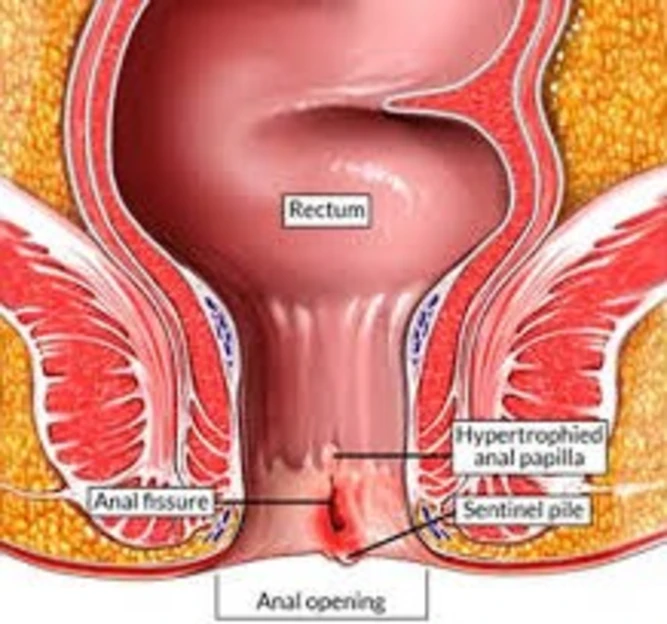
1. Piles -
Also known as hemorrhoids, piles, which require treatment from a skilled piles surgeon, involve enlarged veins affecting the pelvic region or anus. Swelling, bleeding, and irritation can cause extreme discomfort. There are two main categories: internal piles develop within the rectum, while external piles form beneath the skin near the anus.
Although straining during bowel motions, pregnancy, and obesity are risk factors, the exact etiology of piles remains unknown. Fortunately, piles are rarely serious and may usually be controlled with basic household care. This can entail taking more fiber to aid in the dissolution of stools, treating infections with sitz baths, and managing pain with over-the-counter treatments.
Additionally, Laser Piles Treatment in Mathura offers a minimally invasive solution, ensuring effective relief and quicker recovery. For individuals in the region, Laser Piles Treatment in Mathura has become a preferred choice due to its precision and reduced post-surgery discomfort.
Types of Piles :
- Internal piles: Internal piles typically cause no pain and grow inside the rectum. The only times you might consider calling them would be if you notice bright red blood following a bowel movement or if they prolapse (push out) during straining.
- External piles: These can cause a great deal of discomfort as they form beneath the skin and pores surrounding the anus. They could also result in swelling, pain, burning, and itching. There can be a bump next to your anus as well.
Causes of Piles :
- Straining during bowel movements due to stools or diarrhea
- delayed periods of time spent sitting on the toilet
- Pregnancy strains your veins as the growing toddler grows.
- Obesity or being overweight
- Older People, as the tissues that support your veins shrinking with time
- Having a family history of vein problems
- Frequently lifting heavy devices
2. Fissure -
A little hole or fracture in the anal lining is called an anal fissure. Usually, it causes pain and bleeding throughout, especially after bowel movements. This situation is extremely common and can affect individuals of all ages, but it is more prevalent in teenagers and middle-aged adults.
The most common sign of an anal fissure is severe pain during bowel movements, which may continue for hours afterward. Bright pink blood on toilet paper or in the bowl of the toilet could be the first sign of the discomfort, which is commonly described as intense and burning. Some people could also experience a burning or itching feeling all over their anus. Laser Treatment for Anal Fissures in Mathura is an advanced, effective option for managing this condition, offering relief with minimal discomfort and faster recovery times.
Types of Fissures:
Acute Anal Fissures: Usually brought on by an unplanned trauma or injury to the anal canal, they are newly formed fissures. They may heal with alternative therapies because they are often minor. However, severe cases may require anal fissure operation to promote healing.
Chronic Anal Fissures: Anal fissures that last longer than six weeks or that continue to remain during treatment are constantly monitored. Severe cracks may be deeper and offer additional evidence against recovery.
Primary Anal Fissures: These fissures develop on their own without the need for medical intervention. They are often triggered by trauma from tough stool or unnecessary straining during bowel movements.
Secondary Anal Fissures: These small holes are correlated with underlying illnesses that negatively impact the functionality of the lumen of the anal canal, such as chronic inflammatory bowel disease, AIDS or HIV, or other medical issues.
Causes of Fissures:
- Reduced Blood Flow: Disorders like diabetes or cardiovascular disease that affect blood flow to the anal region might hinder healing and increase the risk of fissures.
- Low-Fiber Diet: Never obtaining plenty of fiber could cause you to later become dehydrated, making fissures in your anal more probable.
- Trauma from Hard Stools: One of the most frequent causes of anal fissures is passing large or challenging stools. Fissures may result from the delicate outer layer and pores surrounding the anus straining and tearing.
- Medical Conditions: Due to infection and modifications in bowel conduct, inflammatory bowel diseases consisting of Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis might increase a person’s danger to anal fissures.
- Diarrhea or persistent constipation: Both disorders can also contribute to anal fissures. Prolonged constipation causes straining at some stage in bowel movements, and extended diarrhea can weaken and more difficult the pores on the skin and pores across the anus.
- Anal Trauma: Anal fissures can result from damage to the anal area caused by anal intercourse, overseas object insertion, or trauma sustained at some point of childbirth.
3. Fistula -
A fistula is a remarkable anatomical connection between sections of the body that would not normally be joined. Imagine a microscopic tunnel that burrows into tissues and organs, or perhaps it extends from an organ to the skin’s surface pores. These tunnels allow fluids, such as pus or digestive waste, to flow from one place to another in an undesired manner. Although fistulas can spread throughout the body, the best treatment for fistula involves specialized medical care to effectively close these abnormal pathways and restore normal bodily function. Top Laser Treatment For Fistula in Mathura is one of the most advanced and effective methods for addressing these abnormal connections. The following locations are frequently seen:
- Near the anus: An infected anal gland is connected to the skin and pores around your anus by an anal fistula. This kind is typical and can cause pain and persistent discharge.
- Intestine: Digestive fistula possess the power to join tracts of the bowels or abdomen with another organ, also known as the gall bladder. These often occur after surgery or due to inflammatory bowel disease.
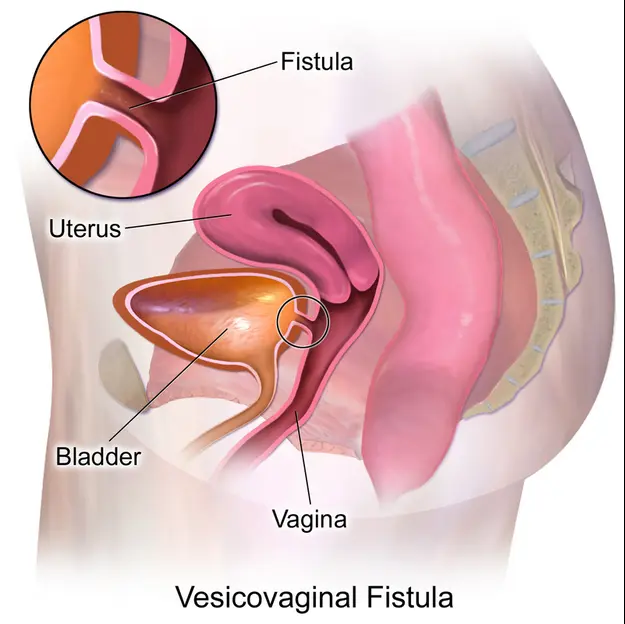
- Bladder: A vesico vaginal fistula, which connects the bladder and vagina, can generate an uneven pathway that allows urine to flow into the vagina.
Types Of Fistula :
- An anal fistula: There is a link between an infected anal gland and the skin and pores surrounding the anus. It is a typical kind of fistula that may cause pain and continuous leakage.
- Intestinal fistula: This particular kind of blood vessels might connect two gastrointestinal tracts or any additional organ, that includes the covering of the skin or abdomen. These are generally a consequence of a condition that causes bowel inflammation (such as Crohn’s illnesses or ulcerative colitis, among others) or follow surgery.
- Rectovaginal fistula: A rectovaginal fistula is an inappropriate passage made between the vagina and the rectum. It could allowed diarrhea to get into the genital tract.
- Colovaginal fistula: This particular kind makes an intersection involving the female reproductive system and the lining of the colon, or big intestinal tract, which is similar to a rectovaginal fistula.
- Enterovaginal fistula: The reason behind this fistula unites the womb to the smaller intestine.
- Vesicovaginal fistula: The following blood vessels forms an unbelievable breach between the female genital tract and the bowel, which allows urine to leak into the inside of the bladder.
Causes of Fistulas :
- Infection: When a blood vessel (a bubble of fluid) cracks, the lymphatic drainage cycle can lead to a fistula.
- Irritation: Colitis with ulcers and Crohn’s disease are both conditions that might trigger persistent inflammation, which may harm structures and leads to the occurrence of a fistula.
- Surgery: A passageway can sometimes appear as a result of complications with surgery.
- Trauma: A physiological injury or trauma might harm tissues and create a link amongst tissues.
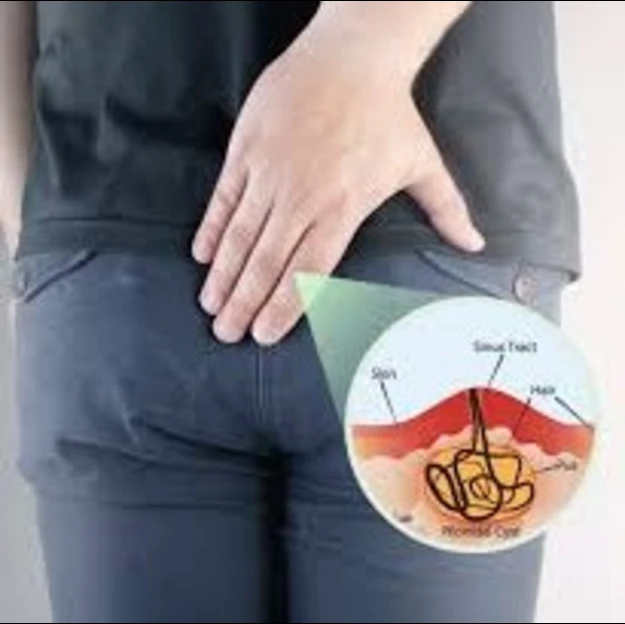
4. Pilonidal sinus -
A painful condition known as a pilonidal sinus, occurring at the top of the buttocks cleft near the tailbone, resembles a tiny hole or tunnel in the skin and can easily become irritated. It may become inflamed, leading to an infection or pilonidal cyst filled with dust, hair, and other particles. This inflammation can cause extreme discomfort, swelling, redness, and pus leakage. Treatment typically involves pilonidal sinus surgery to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Although the precise function of the pilonidal sinus is uncertain, a variety of variables are thought to be involved. Vibration in the area, often caused by prolonged sitting, might force loose hairs or hair growing in that area back into the skin’s pores. This imbedded hair causes the body to react as though it were a splinter, which leads to an inflammatory response.
A tube (tunnel) within the pores and skin may be created by this inflammation, trapping additional hair and other material and increasing the risk of infection and the development of a cyst or infection.
Types Of Pilonidal sinus :
- Stage 1 (Acute Abscess): This is the most uncomfortable stage. A bureaucratic abscess loaded with hair, pus, and dirt. Serious suffering, swelling, redness, and maybe discharge are the cause.
- Stage 2 (Chronic Sinus): A chronic sinus tract may also linger behind the skin’s pores and layers of skin after the initial infection disappears. Once more, this tract may become inflamed, leading to flare-ups in the United States of America with symptoms similar to those of level 1, although frequently less painful.
- Stage 3 (Recurrent An abscess): If the sinus tract isn’t regularly treated completely, an infection can happen continuously. The definition of degree three is this cycle of contamination, repair, and recontamination.
Causes Of Pilonidal sinus :
- Friction and Ingrown Hairs: Loosening hairs or hairs developing in the buttock gap may be forced back into the skin by friction within the cut, sometimes caused by sitting for an extended period. This hidden hair causes its surrounding tissue to react as though it were an injury, which causes an inflammatory reaction.
- Trapped Hair and Debris: This irritation has the potential to develop a tunnel or tract beneath the skin. Greater hair and particles have the potential to become trapped in this tract over time, leading to contamination and illness.
- Risk Factors: A number of variables increase your vulnerability to pilonidal sinus. A deep birth cut, being a man, being a young adult, working in jobs that require a lot of sitting, excessive perspiration, having weight issues, and having personal medical history are a few of these.

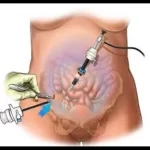
What Is Laparoscopy ?
Examine the indoors of your pelvis or stomach. As a keyhole surgical treatment, a few tiny incisions are made instead of a big one. A doctor makes one of the incisions for the duration of a laparoscopy and slips a thin, illuminated device known as a laparoscope via it. A tiny video digital camera connected to the top of the laparoscope transmits pictures of your interior organs to a show display screen inside the operating room.
This spares you from having to be completely uncovered even as nevertheless allowing the doctor to view the whole lot on a magnified scale. Compared to open surgical treatment, laparoscopy has numerous benefits.Less pain, faster healing, and plenty much less scars are the effects.
It’s moreover regularly related to a discounted risk of infection and reduced blood loss. Laparoscopy serves both recovery and diagnostic capabilities. It lets physicians examine the organs, look for anomalies, and on occasion dispose of tissue samples for biopsies with the intention to make an analysis.
Disease Under Laparoscopy :-
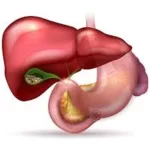
1. Gallstone -
Solid deposits called gallstones develop inside your gallbladder, a bit of an organ close to your liver. The liver produces bile, a digestive fluid that the gallbladder is answerable for storing. Bile aids within the small intestine’s breakdown of lipids. Bilirubin, a waste made from pink blood cells, or a mixture of the 2 can shape gallstones. They range in length from minuscule to big, similar to a golfing ball.
The majority of gallstone patients don’t show any signs. On the other hand, an acute and extreme discomfort on your higher returned or upper proper stomach, immediately beneath your shoulder blade, can also occur if a gallstone obstructs a bile duct. This ache may continue for hours or minutes and might start after a fatty meal.
Detection and intervention can lessen the hazard of issues. Surgery to take away the gallbladder is typically required as part of the remedy for gallstones. This is a recurring operation with a short recuperation duration.
Types Of Gallstone :
- Cholesterol gallstones: Gallstones as a result of ldl cholesterol are the most frequent kind, making up around 80% of all gallstones. They broaden when your bile incorporates immoderate quantities of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in evaluation to lecithin and bile salts, which normally keep ldl cholesterol dissolved. Gallstones due to cholesterol generally have a yellowish-green look.
- Pigment gallstones: Less often than ldl cholesterol gallstones, pigment gallstones increase while the waste product bilirubin—that is produced whilst purple blood cells spoil down—is present in extra in your bile. Gallstones from pigment are frequently dark brown or black in color. People with precise clinical issues, inclusive of sickle cellular disorder or liver cirrhosis, are much more likely to experience them.
Causes Of Gallstone :
- Over consumption of ldl cholesterol: Bile generally has enough substances to preserve ldl cholesterol’s dissolution. However, cholesterol can precipitate out of solution and shape crystals in case your liver produces an excessive amount of cholesterol or in case your bile is deficient in bile salts. Gallstones can also sooner or later form from the clustering of those crystals
- Excessive bilirubin production: When red blood cells spoil down, your frame releases bilirubin as waste. A range of diseases, which includes blood disorders and liver sickness, can increase the amount of bilirubin in your bile. This also can lead to pigment-made gallstones, which can be frequently dark brown or black in color.
- Gallbladder disease: If your gallbladder is not emptying often, your bile can be listening and boozing, which increases the hazard of gallstone formation..
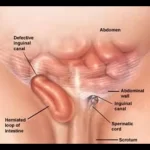
2. Inguinal Hernia-
The area wherein your thigh and lower stomach meet is called the groin. This weak point can be there from delivery or may additionally expand over time due to muscle strain.
Your intestines or fat might also protrude from the bulging tissue. An obvious bulge inside the groin is regularly the result of an inguinal hernia. Whenever you cough, strain, or lift heavy items, this bulge should get bigger. Additionally, specifically when accomplishing these activities, you can sense ache or soreness within the groin region.
Treatment for Inguinal Hernia in Mathura is available to effectively address this condition, providing relief and preventing further complications.
Types Of Inguinal Hernia :
- Direct inguinal hernia: This type of hernia takes place while stomach tissue pushes into the groin canal through a weak spot within the belly wall. Adults are more likely to develop direct inguinal hernias, in particular if they have a record of heavy lifting or straining.
- Indirect inguinal hernia: The most customary type of inguinal hernia is an oblique one, which occurs while tissue pushes through an innate weakness inside the groin canal that exists from delivery. Men are more likely than girls to revel in an oblique inguinal hernia, that may manifest at any age.
Causes Of Inguinal Hernia :
- Weakness in the abdominal wall: This weak point may arise steadily over time or be congenital. Congenital inguinal hernias arise while the inguinal canal, a passageway inside the lower stomach wall, partly opens earlier than beginning. The belly wall may additionally grow to be weaker with time due to problems that affect collagen, growing old, or earlier groin surgery.
- Increased pressure within the abdomen: A growth in abdominal pressure Numerous conditions and behaviors, inclusive of severe exercise, persistent sneezing or coughing, constipation, obesity, and being pregnant, might result in this pressure. By placing extra stress on the abdomen, straining in the course of bowel motions or urine also can propose an inguinal hernia.
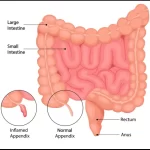
3. Appendix -
The appendix is a tiny, finger-formed pouch placed within the backside right part of your abdomen that is linked to your large intestine. It is generally between two and four inches lengthy, about the size of a bug. Scientists think the appendix may additionally have helped our ancestors with digesting, even supposing its unique purpose continues to be relatively unknown. According to a few hypotheses, it functioned as an area to shop for appropriate gut microorganisms, which aid immunological and digestive procedures.
The appendix is a tiny, finger-formed pouch placed within the backside right part of your abdomen that is linked to your large intestine. It is generally between two and four inches lengthy, about the size of a bug. Scientists think the appendix may additionally have helped our ancestors with digesting, even supposing its unique purpose continues to be relatively unknown.
Types Of Appendix :
- Acute appendicitis: The most common sort of appendicitis is known as acute because it produces an abrupt and extreme irritation of the appendix. Usually, signs and symptoms seem swiftly over a few hours.
- Chronic appendicitis: A less common sort of appendicitis that produces mild, recurrent pain in the decreased proper abdomen is known as chronic appendicitis. Weeks or months may also skip with the ache coming and going.
Causes Of Appendix :
- Hardened stool (fecaliths): These are small, hard pieces of stool that can get lodged in the opening of the appendix.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the abdomen
- Infection in the digestive tract
- Foreign objects (rare)
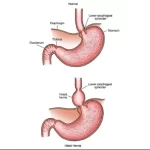
4. Hiatus Hernia -
A hiatal hernia occurs while part of your stomach is punctured by the diaphragm, the muscle that divides your chest and stomach. The tube that incorporates food from your mouth for your stomach, the esophagus, can match past the tiny starting of the diaphragm. If you have got a hiatal hernia, the stomach pushes through this hollow and into the hole vicinity on your chest.
This is an alternatively common occurrence, especially many of the over-50 set. Usually, there are not any overt signs or indicators. When they do, but, normally have acid reflux sickness because of the reason. Acid reflux, the fruits of belly acid backing up into the throat, causes heartburn, or a burning feeling to your chest.
Best Hiatal Hernia Treatment/Surgery in Mathura offers specialized care for managing and correcting this condition, ensuring relief and restoration of normal function.
Types Of Hiatus Hernia :
- Paraesophageal Hiatus Hernia (Rolling Hiatus Hernia): In this form, the stomach herniates through the esophageal hiatus and rests subsequent to the esophagus, but the gastroesophageal junction stays in place.
- Mixed Hiatus Hernia: This kind consists of factors of both paraesophageal and sliding hernias. Any different part of the belly can herniate alongside the esophagus, but the gastroesophageal junction and a part of the stomach circulate into the chest. Short Esophagus: This less frequent type causes the belly to draw into the esophagus because of a congenitally quick esophagus.
Causes Of Hiatus Hernia :
- Being born with an unusually large hiatus.
- Injury or trauma to the area such as force from a seatbelt during an accident.
- Obesity.
- Persistent and intense pressure on the surrounding muscles caused by: Chronic coughing. Lifting heavy objects. Repetitive vomiting. Straining during a bowel movement.
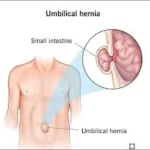
5. Umbilical Hernia -
The character with a hernia can have a bulge close to their stomach button, which may additionally enlarge after they cry, cough, or stress. By the time an infant is one or two years antique, umbilical hernias frequently close on their own. Increased stomach stress from situations together with obesity, heavy lifting, numerous pregnancies, or continual coughing can cause an umbilical hernia in adults.
Adults with umbilical hernias have a decreased propensity for spontaneous resolution than infants do, Therefore, umbilical hernia surgery becomes crucial to avoid complications. Adults who have an untreated umbilical hernia run the hazard of strangulation, a medical emergency requiring instantaneous attention, wherein the herniated tissue turns into imprisoned and loses its blood supply. Repairing the stomach wall defect and putting the sticking out tissue lower back into vicinity are the surgical treatments for umbilical hernias.
Types Of Umbilical Hernia :
- Reducible umbilical hernia: This is the most common kind. The bulge due to the intestine or fatty tissue pushing through the belly wall can be without problems pushed lower back in through a doctor.
- Incarcerated umbilical hernia: In this situation, the bulge cannot be driven back into the stomach. This can reason ache and tenderness in the vicinity around the bulge. It’s vital to seek scientific attention immediately in case you enjoy this.
- Strangulated umbilical hernia: Whilst strangulation is a noticeably uncommon hardship of hernias it may occur with any type of hernia. Strangulation chance is probably best with femoral hernias.
Causes oF Umbilical Hernia :
- Obesity
- Multiple pregnancies
- Ascites (excess fluid in the abdomen)
- Chronic cough
- Straining during heavy lifting or bowel movements
6. Diagnostic Laparoscopy -
A diagnostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical operation that allows scientific professionals to take a look at the inner of your abdomen or pelvis. A scientific expert creates a tiny incision to your belly or stomach button throughout the method so that you can insert a skinny, illuminated tube called a laparoscope.
You can view an image of your organs on a display in the running room way to the tiny video camera on the end of this laparoscope. Reasons: A doctor may endorse a diagnostic laparoscopy for a whole lot of motives.
Best Diagnostic Laparoscopy Surgery in Mathura offers advanced, precise diagnostic solutions for patients, ensuring minimal discomfort and a quicker recovery.
Types Of Diagnostic Laparoscopy :
- Abdominal laparoscopy: This manner focuses on inspecting the organs in the abdomen, together with the appendix, liver, gallbladder, intestines, and stomach.
- Pelvic laparoscopy: This manner specializes in analyzing the organs within the pelvis, which include the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and bladder. It’s broadly speaking executed on ladies.
Causes Of Diagnostic Laparoscopy :
- Pelvic ache: Pain for your pelvis will be caused by quite a few situations, which includes urinary tract infection, kidney stones, hernia, or digestive troubles. Pain inside the proper side may additionally indicate appendicitis, that is a medical emergency.
- Inexplicable stomach ache: Chronic stomach pain is pain that is present for more than three months. It may be present all of the time (persistent) or come and go (routine). Chronic abdominal pain can occur in children any time after age five years. Some kids aged 5 to sixteen years, specially the ones aged 8 to 12 years, have chronic or recurring belly ache.
- Abnormal growths: A diagnostic laparoscopy might be applied to acquire a deeper know-how if a health practitioner feels a lump for your stomach or pelvis for the duration of a bodily exam or if imaging assessments screen a regular upward push.